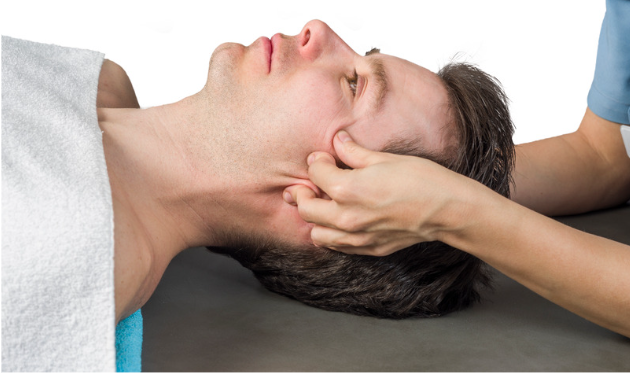
Also known as craniosacral therapy, Cranial Sacral Therapy is a hands-on technique that alleviates tension in the cranial bones, the spine, and the sacrum (the small, triangular bone just above the coccyx). CST is considered a non-invasive technique. The therapist applies gentle pressure on the patient’s back, neck, and head, in order to relieve compression in these bones, and therefore alleviate the stress and the pain it causes. This is how CST manages to alleviate the symptoms of a wide array of medical conditions.
A possible explanation of these benefits is that the gentle manipulation of the skull bones, spinal vertebrae and pelvis leads to a normalization of the cerebrospinal fluid flow in the central nervous system. The removal of these “blockages,” results in an enhanced ability of the body to self-heal.
With proper training, chiropractors, osteopaths, massage therapists, and physical therapists are able to perform craniosacral therapy, either as part of a more comprehensive treatment or as a stand-alone procedure. Depending on the problem you’re trying to sort out with CST, you may need between three and ten therapy sessions, followed by maintenance ones. Your therapist will assess your condition and will recommend the ideal routine for you.
Benefits
CST helps to encourage the relief of compression in the head, neck, and back. This can alleviate pain, stress, and emotional tension. In addition, it may have physical benefits such as restoring cranial mobility and removing blockages in the head, neck, and nerves.
Patients of all ages may be eligible for cranial sacral therapy. Here are a few of the conditions it can address:
- headaches and migraine
- sleep troubles
- sinus and ear infections
- constipation
- IBS
- depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders
- TMJ
- fibromyalgia
- scoliosis
- pregnancy-related issues
Even though anecdotal evidence shows that cranial sacral therapy works, in order to prove its benefits beyond doubt, more scientific studies are needed to build a foundation of empirical evidence. According to some studies, CST may only be effective in younger patients such as children, toddlers, and infants. However, there are also cases of stress and tension alleviation in older patients. Other studies have found that cranial sacral therapy is effective for certain medical conditions only. According to a Trusted Source study from 2012, CST is very powerful in alleviating severe migraine symptoms. Another study evidenced a significant symptom relief in patients with fibromyalgia.
Potential Side Effects
In terms of side effects, the most common one is a temporary mild discomfort that decreases and fades away within the first 24 hours after the treatment. There are people who aren’t eligible for CST. Patients with diagnosed aneurysms, individuals with severe bleeding problems, or with recent traumatic head injuries or head bone fractures shouldn’t use cranial sacral therapy.
Technique
During your first appointment, the therapist will ask you about your symptoms and about any medical issues you may have. You typically won’t need to remove your clothes during the therapy, so make sure you wear something comfortable. Most likely you’ll be lying down, face-up on the massage table. Stand-alone CST sessions typically last about 60 minutes, but they can also be combined with other modalities.
Some practitioners may start working your body from the head, others may prefer to start from your feet, then move to the spinal cord, and then work their way up to your skull. The therapist applies gentle pressure on your body. This pressure is equivalent to the weight of a small coin. You’ll only feel this gentle weight as the practitioner holds your feet, your sacrum, or your head. In some situations, the practitioner may detect that they need to reposition your body to normalize the cerebrospinal fluid flow. More often than not, therapists use tissue-release methods to achieve this, while supporting one of your legs.
Different patients may experience different sensations during the treatment. The most frequent sensations include a deep relaxation feeling, pulsations, hot or cold sensations, or numbing. Cranial sacral therapy may work very well in certain medical conditions such as headaches (with some scientific evidence supporting this claim). Thanks to the very low risk of side effects, CST is the choice of many patients who don’t want to put up with the risks or potential side effects of other pain relief alternatives.